Dupa plasarea solicitării de comandă, in sectiunea Istoric puteti vedea cate solicitări de comandă mai avem de procesat inaintea dumneavoastra
Program de lucru: Luni - Vineri 9:00 - 18:00, pauza 13:00 - 14:00.
Se efectueaza lucrari de mentenanta la site si pot aparea erori. In cazul in care intampinati erori va rugam sa reincercati mai tarziu.
Ridicarea personala este disponibila pentru comenzile achitate in avans. Se pot ridica dupa ce sunt pregatite.
Niciun produs
 Mărește
Mărește
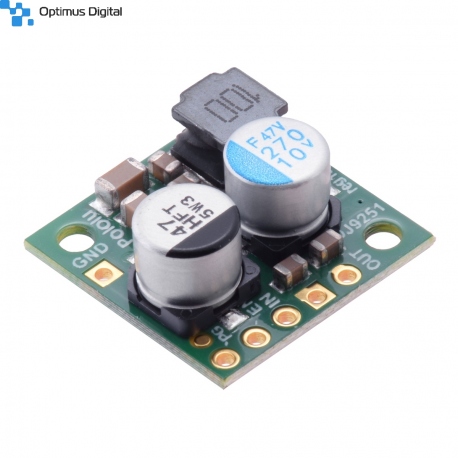
Sursă Step-Down Pololu D24V22F7 de 7.5 V, 2.4 A (coborâtoare)
0104110000010391
Produs nou
Sursă Step-Down Pololu D24V22F7 de 7.5 V, 2.4 A ce permite obținerea unei astfel de tensiuni din surse de alimentare mai mari, de până la 36V.
1 bucata in stoc
Ultimele bucăți în stoc
- Scrie o recenzie
- Elimina acest produs din lista mea de favorite.
- Adauga acest produs la lista mea de favorite.
- Imprimă
Informații
Caracteristici tehnice:
- Tensiune de intrare: 8V - 36V (minim 8.5V pentru curent de ieșire de 2.4A);
- Tensiune de ieșire: 7.5V;
- Acuratețe tensiune de ieșire: 4%;
- Curent maxim de ieșire: 2.4A;
- Curent de scurgere maxim, în gol: 3mA;
- Eficiență: 85% - 95%;
- Frecvență de funcționare: 400kHz;
- Protecție la alimentare inversă, supracurent și supratemperatură.
Dimensiuni: 17.8 × 17.8 × 8 mm.
Acest produs reprezintă o sursă de tensiune de stabilizează tensiuni de până la 36V la o tensiune de ieșire de 7.5V. Curentul maxim furnizat de această sursă este de 2.4A, suficient pentru a alimenta mai multe circuite simple folosite în proiectele dumneavoastră.
The source works in switching with up to 95% efficiency, so it dissipates very little heat and can be included in any project.
See the manufacturer's page for more details .
Recenzii
Clienții care au cumpărat acest produs au mai cumpărat:
-

Cablu GPIO...
Modul cu 40 de contacte pentru Raspberry PI.
$1.56
-

Tranzistor...
Componenta electronica ideala pentru circuitele...
$0.04
-
Tranzistor...
Tranzistor IRFU9024PBF
$1.08
-
Placă de...
Placă de Test Universală Verde 50x70 mm
$0.48
-

Dispozitiv...
Dispozitiv de cuplaj pentru servomotoare.
$0.60
-

Servomotor...
Acest servomotor brushless este ideal pentru...
$86.16
-

Sursă Pololu...
Sursă Pololu Step-Down D24V10F5 de 5 V, 1 A...
$15.84
-

Set...
Un kit complet de conectori: headere de pini...
$14.40
-

Cablu...
Cablu Alimentare Euro LA IEC C7 (Casetofon) 2...
$1.92
-

Sursă de...
Această sursă de tensiune de tip...
$20.40






