Dupa plasarea solicitării de comandă, in sectiunea Istoric puteti vedea cate solicitări de comandă mai avem de procesat inaintea dumneavoastra
Program de lucru: Luni - Vineri 9:00 - 18:00, pauza 13:00 - 14:00.
Se efectueaza lucrari de mentenanta la site si pot aparea erori. In cazul in care intampinati erori va rugam sa reincercati mai tarziu.
Ridicarea personala este disponibila pentru comenzile achitate in avans. Se pot ridica dupa ce sunt pregatite.
No products
 View larger
View larger
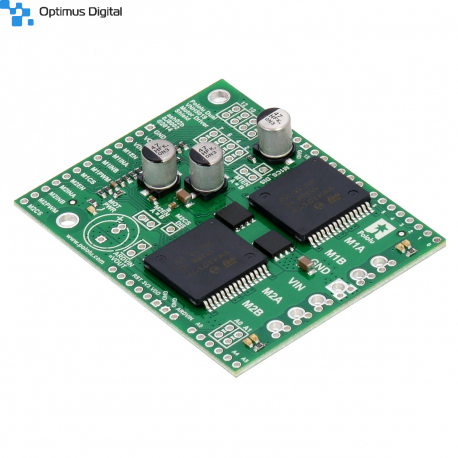
Pololu Dual VNH5019 Motor Driver Shield for Arduino
0104110000027733
New product
This shield makes it easy to control two high-power DC motors with your Arduino or Arduino-compatible board. Its dual robust VNH5019 motor drivers operate from 5.5 to 24 V and can deliver a continuous 12 A (30 A peak) per motor, or a continuous 24 A (60 A peak) to a single motor connected to both channels. These great drivers also offer current-sense feedback and accept ultrasonic PWM frequencies for quieter operation. The Arduino pin mappings can all be customized if the defaults are not convenient, and the motor driver control lines are broken out along the left side of the shield for general-purpose use without an Arduino.
See description for more details about the product.
Add to cart now!
This product is no longer in stock
- Write a review
- Remove this product from my favorite's list.
- Add this product to my list of favorites.
More info
Overview
This motor driver shield and its corresponding Arduino library make it easy to control two bidirectional, high-power, brushed DC motors with an Arduino or compatible board. The board features a pair of robust VNH5019 motor drivers from ST, which operate from 5.5 to 24 V and can deliver a continuous 12 A (30 A peak) per channel, and incorporates most of the components of the typical application diagram on page 14 of the VNH5019 datasheet (475k pdf), including pull-up and protection resistors and FETs for reverse battery protection.
This versatile motor driver is intended for a wide range of users, from beginners who just want a plug-and-play motor control solution for their Arduinos (and are okay with a little soldering) to experts who want to directly interface with ST’s great motor driver ICs. The Arduino pin mappings can all be customized if the defaults are not convenient, and the VNH5019 control lines are broken out along the left side of the board for general-purpose use without an Arduino (see the right connection diagram below). This versatility, along with an option to power the Arduino directly from the shield, sets this board apart from similar competing motor shields.
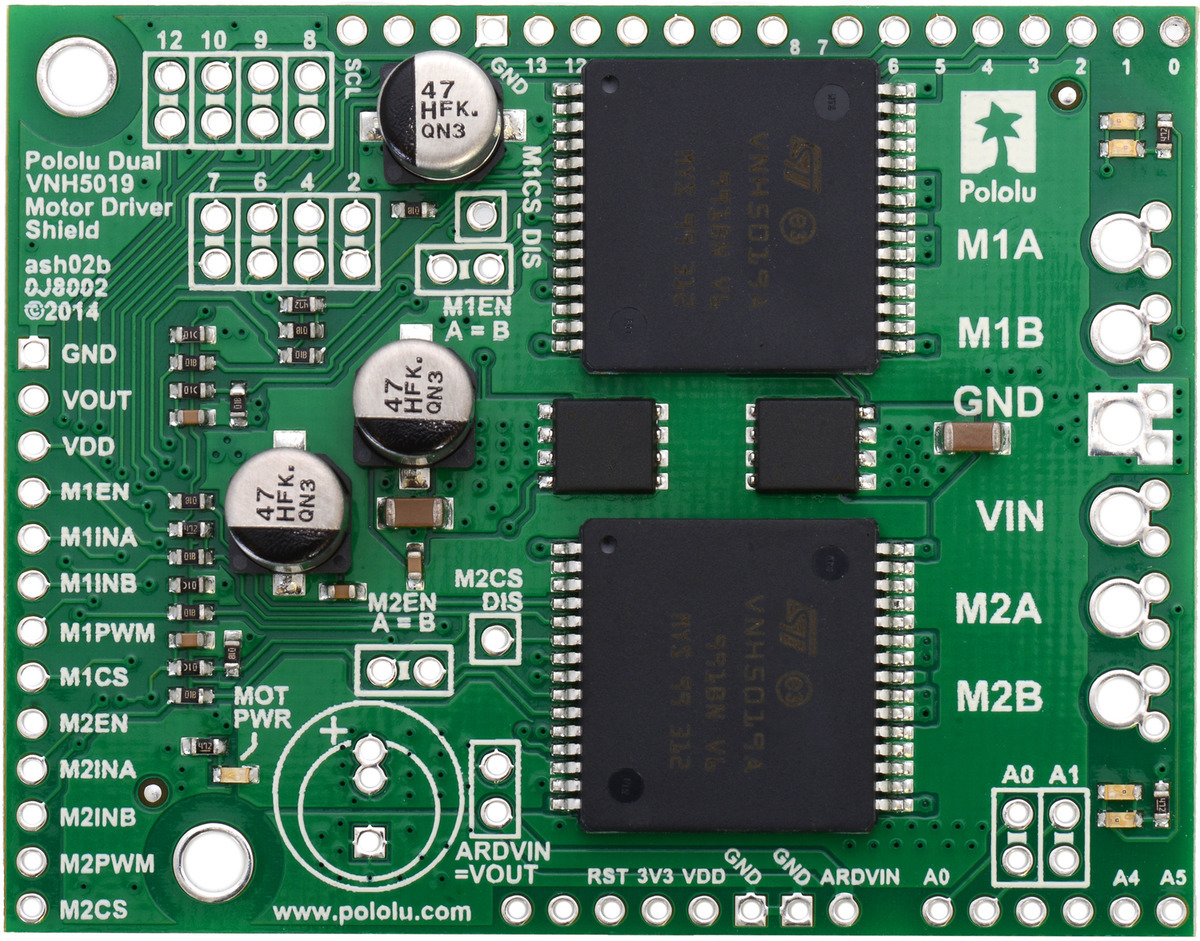
Pololu dual VNH5019 motor driver shield for Arduino.
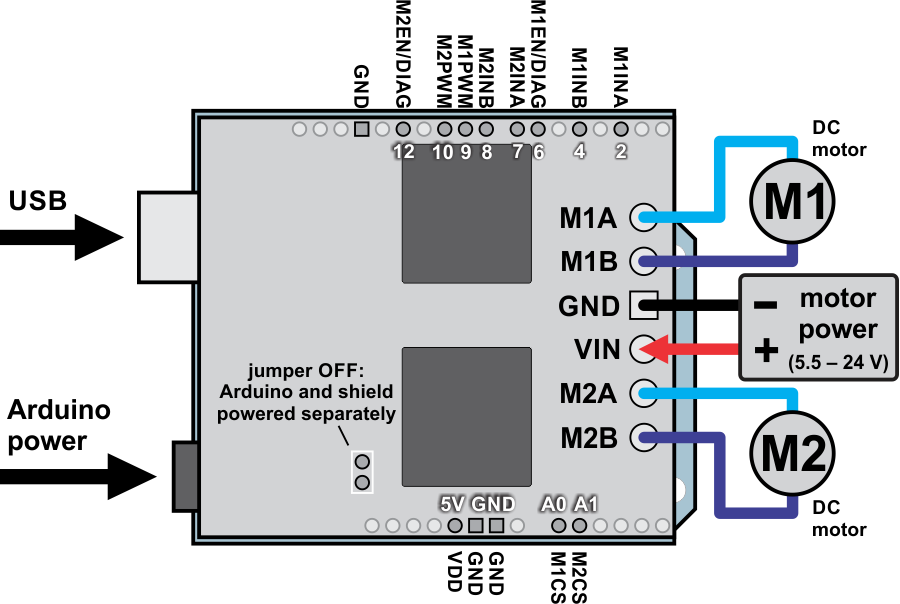
Dual VNH5019 motor driver shield with an Arduino (shield and Arduino powered separately).
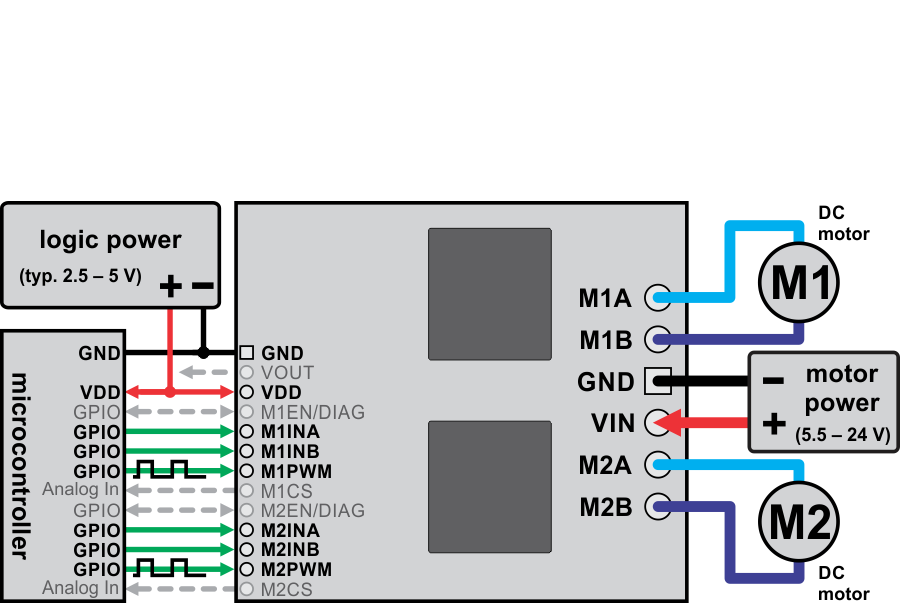
Dual VNH5019 motor driver shield connected to a microcontroller (gray connections are optional).
Features
• Wide operating voltage range: 5.5 – 24 V1
• High output current: up to 12 A continuous (30 maximum) per motor
• Motor outputs can be combined to deliver up to 24 A continuous (60 A maximum) to a single motor
• Inputs compatible with both 5V and 3.3V systems (logic high threshold is 2.1 V)
• PWM operation up to 20 kHz, which is ultrasonic and allows for quieter motor operation
• Current sense voltage output proportional to motor current (approx. 140 mV/A; only active while H-bridge is driving)
• Motor indicator LEDs show what the outputs are doing even when no motor is connected
• Can be used with an Arduino or Arduino clone (through shield headers) or other microcontroller boards (through 0.1" header along the left side)
• When used as a shield, the motor power supply can optionally be used to power the Arduino base as well
• Arduino pin mappings can be customized if the default mappings are not convenient
• Arduino library makes it easy to get started using this board as a motor driver shield
• Detailed user’s guide
• Reverse-voltage protection to -16 V
• Robust drivers:
○ Can survive input voltages up to 41 V
○ Undervoltage and overvoltage shutdown
○ High-side and low-side thermal shutdown
○ Short-to-ground and short-to-Vcc protection
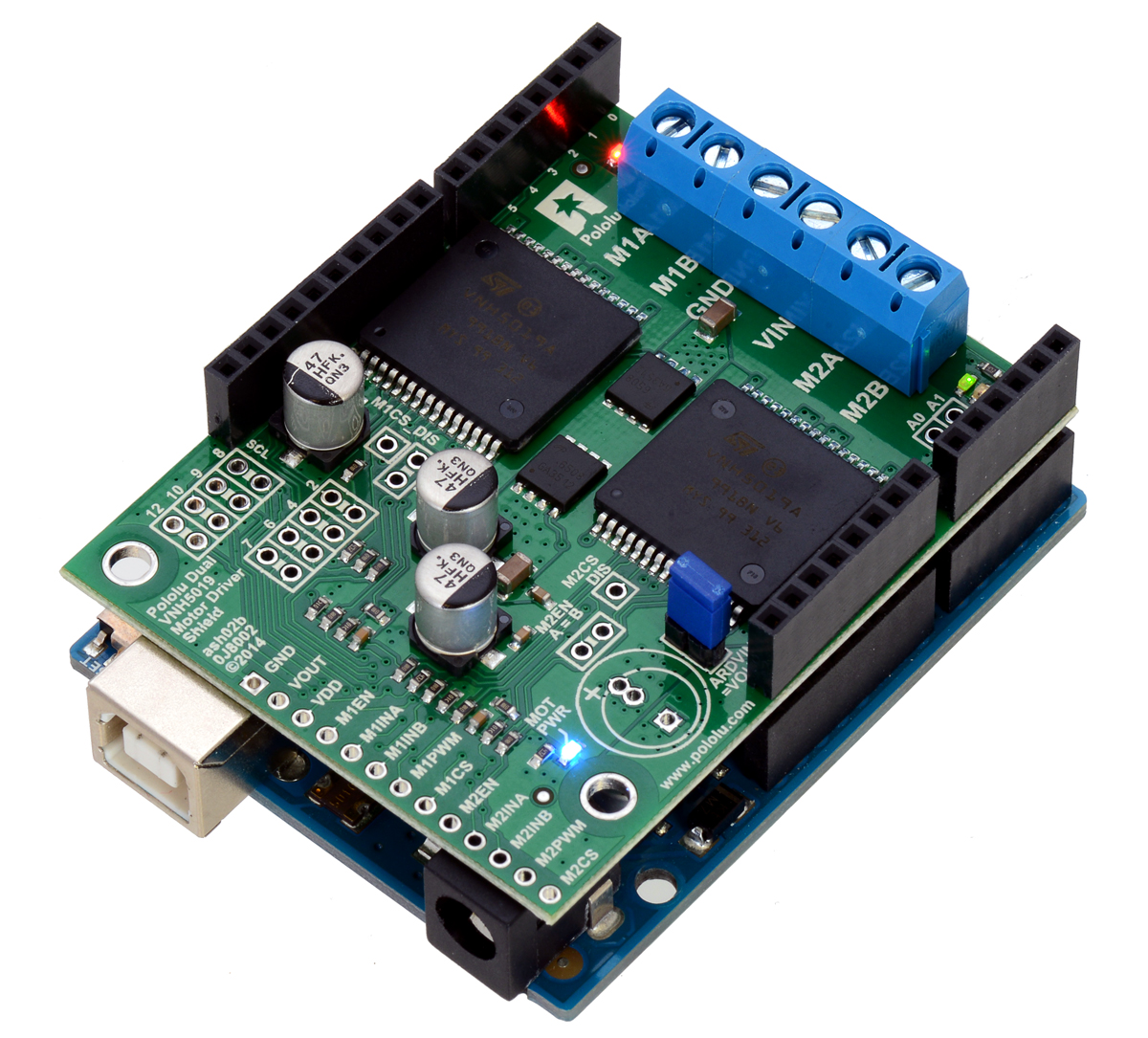
Pololu dual VNH5019 motor driver shield, assembled and connected to an Arduino Uno R3.
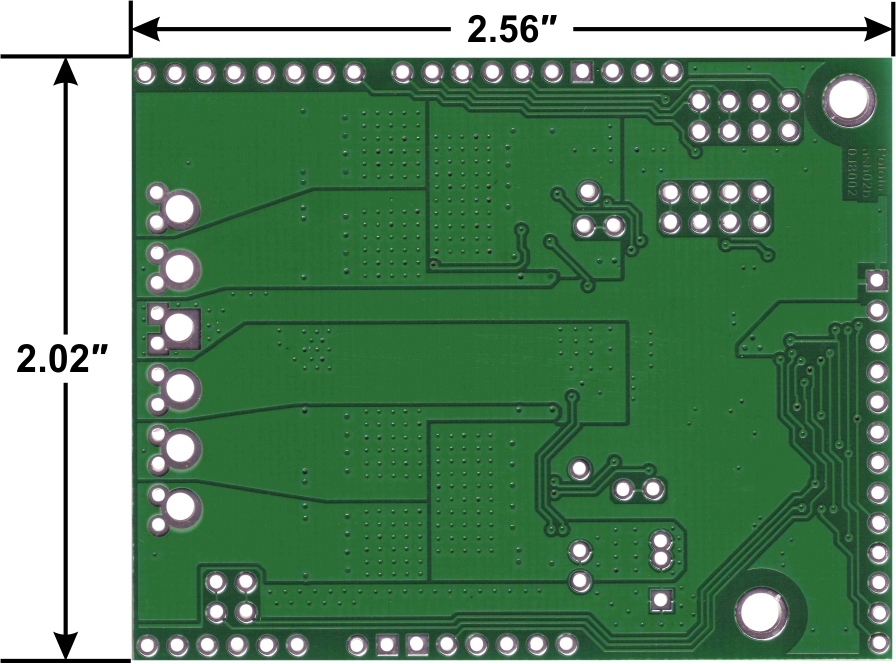
Pololu dual VNH5019 motor driver shield for Arduino, bottom view with board dimensions.
1 While the overvoltage protection typically kicks in at 27 V, it can trigger at voltages as low as 24 V, so we do not recommend using this motor driver with 24 V batteries, which significantly exceed 24 V when fully charged. If the shield is configured to power an Arduino or Arduino clone, the supply voltage must conform to that Arduino’s input voltage requirements.
Schematic Diagram
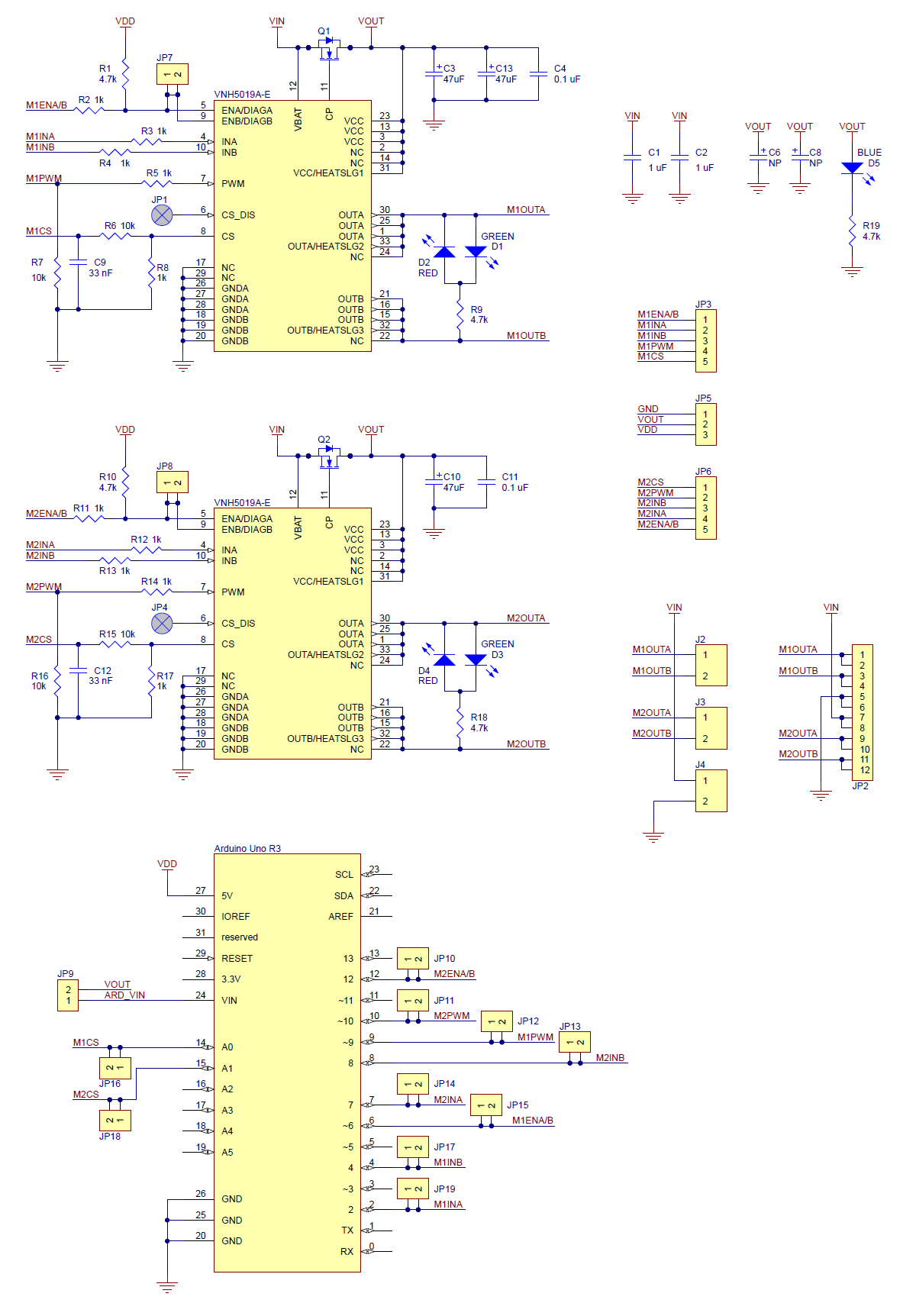
Schematic diagram of the Pololu dual VNH5019 motor driver shield for Arduino.
This schematic is also available as a downloadable pdf: dual VNH5019 motor driver shield schematic (356k pdf)
VNH3SP30, VNH2SP30, and VNH5019 Comparison
The following table offers a comparison of the single-carrier versions of all three drivers:
| VNH3SP30 | VNH2SP30 | VNH5019 | |
| Operating voltage: (1) | 5.5 – 16 V (2) | 5.5 – 16 V | 5.5 – 16 V |
| MOSFET on-resistance (per leg): | 34 mΩ typ. | 19 mΩ max. | 18 mΩ typ. |
| Max PWM frequency | 10 kHz | 20 kHz | 20 kHz |
| Current sense | n/a | 0.13 V/A typ. | 0.14 V/A typ. |
| Over-voltage shutoff | 36 V min. (2) / 43 V typ. | 16 V min. / 19 V typ. | 24 V min. / 27 V typ. |
| Logic input high threshold | 3.25 V min. | 3.25 V min. | 2.1 V min. |
| Time to overheat at 20 A (3) | 8 s | 35 s | 20 s |
| Time to overheat at 15 A (3) | 30 s | 150 s | 90 s |
| Current for infinite run time (3) | 9 A | 14 A | 12 A |
1 The VNH3SP30 can survive input voltages up to 40 V, and the VNH2SP30 and VNH5019 can survive input voltages up to 41 V, but the over-voltage shutoff will kick in at lower voltages.
2 While VNH3SP30’s over-voltage shutoff doesn’t activate until 36 V, in our experience, shoot-through currents make PWM operation impractical above 16 V.
3 Typical results using the Pololu motor driver carrier boards with 100% duty cycle at room temperature (with no forced airflow or heat sinking beyond the carrier PCB).
Real-world power dissipation consideration
Each motor driver IC has a maximum continuous current rating of 30 A. However, the chips by themselves will overheat at lower currents (see the table above for typical values). The actual current you can deliver will depend on how well you can keep the motor drivers cool. The shield’s printed circuit board is designed to draw heat out of the motor driver chips, but performance can be improved by adding heat sinks. In our tests, we were able to deliver short durations (on the order of milliseconds) of 30 A and several seconds of 20 A without overheating. At 6 A, the chip gets just barely noticeably warm to the touch. For high-current installations, the motor and power supply wires should also be soldered directly instead of going through the supplied terminal blocks, which are rated for up to 16 A.
This product can get hot enough to burn you long before the chip overheats. Take care when handling this product and other components connected to it.
Many motor controllers or speed controllers can have peak current ratings that are substantially higher than the continuous current rating; this is not the case with these motor drivers, which have a 30 A continuous rating and over-current protection that can kick in as low as 30 A (50 A typical). Therefore, the stall current of your motor should not be more than 30 A. (Even if you expect to run at a much lower average current, the motor can still draw short bursts of high currents, such as when it is starting, if special steps are not taken.)
Current sense outputs
The voltages on the M1CS and M2CS pins are each approximately equal to 140 mV per amp of output current of the corresponding motor. The current sense readings are more accurate at higher currents. Note that the output is only active while the H-bridge is driving; it is inactive (low) when the driver is coasting (motor outputs are high impedance) or braking. During the coast portion of the drive/coast cycle, current will continue to circulate through the motor, but the voltage on the FB pin will not accurately reflect the motor current.
The current sense output pins are designed for PWM frequencies of 5 kHz or higher. If you use a PWM frequency lower than 5 kHz and want to measure the current, we recommend adding an extra capacitor between the current sense output pin and GND to smooth out the signal. For example, if you use a PWM frequency of 490 Hz and want to measure the current of M1, you should add a 1 µF capacitor (or larger) between M1CS and GND.
Note that while the M1CS and M2CS voltages can potentially exceed 3.3 V at high currents, the current sense circuit should be safe for use with many 3.3V analog inputs. Most MCUs have integrated protection diodes that will clamp the input voltage to a safe value, and since the CS circuit has a 10 kΩ resistor in series with the output, only a few hundred microamps at most will flow through that diode.
Specifications
Dimensions
| Size: | 2.56" x 2.02" x 0.38"1 |
| Weight: | 18 g1 |
General specifications
| Motor driver: | VNH5019 |
| Motor channels: | 2 |
| Minimum operating voltage: | 5.5 V |
| Maximum operating voltage: | 24 V2 |
| Continuous output current per channel: | 12 A |
| Peak output current per channel: | 30 A |
| Current sense: | 0.14 V/A |
| Maximum PWM frequency: | 20 kHz |
| Reverse voltage protection?: | Y3 |
Notes:
1 Without included hardware.
2 Not recommended for use with 24V batteries.
3 To -16 V. Connecting supplies over 16 V in reverse can damage the motor driver.
Don't delay, buy today.
Add to cart now!
Reviews
Customers who bought this product also bought:
-

Development...
Development Board Compatible with Arduino MEGA...
$22.17
-

Ball Caster
Ball Caster See description for more details...
$0.95
-

10p Long...
10p Long Female Pin Header See description for...
$0.29
-

Pololu Dual...
This add-on board makes it easy to control two...
$107.76
-

HC-05 Master...
The HC-05 Bluetooth module is a high...
$6.74
-

L298N Dual...
The L298N engine driver module is ideal for...
$2.64
-

Black...
Black Aluminium V-Slot Profile 2040 (30 cm)
$8.40
-

Pololu 5V,...
This small synchronous switching step-down (or...
$79.68
-
Development...
Development Board Compatible with Arduino UNO...
$9.45
-
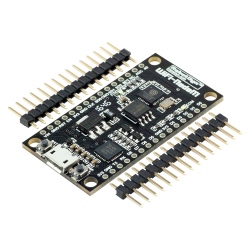
Wemos Micro...
NodeMCU is an open source IoT platform. It...
$7.92






